Top Polyester Yarn Types and Their Uses in Modern Textile Industry?
In the modern textile industry, polyester yarn has emerged as a staple fiber choice. Experts like Dr. Sarah Reed, a renowned textile engineer, emphasize its versatility, stating, "Polyester yarn is revolutionizing fabric production." This synthetic fiber is praised for durability and strength, making it suitable for various applications.
Polyester yarn comes in different types, each serving specific purposes. For example, draw-textured yarns are vital in activewear due to their elasticity. On the other hand, filament yarns create smooth, elegant textiles. Despite its advantages, the environmental impact of polyester remains a concern. Recycling options exist, yet many still land in landfills.
The shift towards sustainability reflects the industry's need for improvement. Development of innovative, eco-friendly alternatives has begun but is not widespread. As the demand for polyester yarn grows, ongoing reflections on its environmental footprint become crucial. Each advancement must align with ecological responsibilities.

Overview of Polyester Yarn and Its Importance in Textiles
Polyester yarn plays a crucial role in the modern textile industry. It is a synthetic fiber known for its strength and durability. According to a report by the Textile World, polyester accounted for over 52% of global fiber production in 2021. This significant figure highlights polyester's dominance in textiles.
The yarn's versatility is evident in its various applications. It is commonly found in clothing, home textiles, and industrial fabrics. In performance apparel, polyester's moisture-wicking properties enhance comfort. Reports indicate that around 30% of activewear incorporates polyester yarn. This fiber's resistance to shrinking and stretching makes it a preferred choice for many manufacturers.
Despite its advantages, polyester also has drawbacks. The environmental impact of producing polyester raises concerns. Microfiber pollution from washing polyester fabrics is an issue many are beginning to address. The industry faces pressure to develop more sustainable practices. As polyester continues to dominate, it is essential for stakeholders to reflect on these challenges and work towards solutions.
Different Types of Polyester Yarn: Characteristics and Variations
Polyester yarns come in various types, each with unique characteristics. The most common types are filament and staple yarns. Filament yarns are smooth and shiny, often used in fabrics requiring sheen. They are durable and resistant to wrinkles. Conversely, staple yarns consist of shorter fibers. They have a textured surface and provide a softer feel. This can enhance comfort in clothing.
Another significant category is textured polyester yarn. These yarns are twisted and crimped, creating a bulkier appearance. They offer stretch and softness, making them ideal for activewear. Then there's recycled polyester yarn, an eco-friendly alternative. It is made from recycled materials and helps reduce waste. This yarn maintains good strength but may vary in quality depending on the source.
Each type has strengths and weaknesses. For example, the sheen of filament yarn may not be suitable for all designs. Some manufacturers struggle with consistency in recycled yarns. It's essential to choose the right type based on your project needs. Understanding these variations can significantly impact the final product's quality and performance in today's textile industry.
Top Polyester Yarn Types and Their Uses in Modern Textile Industry
Common Uses of Polyester Yarn in Fashion and Apparel
Polyester yarn is a versatile material widely used in the fashion and apparel industry. It stands out for its durability and resistance to shrinking and stretching. Many designers appreciate it for its ability to hold vibrant colors. This makes it ideal for creating activewear and sports apparel. Gym clothes often use polyester for its moisture-wicking properties. This helps keep wearers dry and comfortable during workouts.
In addition to activewear, polyester yarn is popular in casual and formal garments. It blends easily with other fibers, enhancing overall fabric performance. For instance, a polyester-cotton blend offers breathability with added strength. However, some people find that polyester can feel less breathable compared to natural fibers. This can lead to discomfort in warm conditions, raising questions about its widespread use.
Polyester’s easy maintenance is another reason for its popularity. It resists wrinkles and requires less ironing. Yet, the environmental impact of polyester production invites criticism. The process can be energy-intensive and may involve harmful chemicals. As the industry evolves, reflections on sustainable practices are crucial. Many are now seeking eco-friendly alternatives while appreciating the unique qualities of polyester yarn.
Top Polyester Yarn Types and Their Uses in Modern Textile Industry
| Yarn Type | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Polyester Filament Yarn | Smooth, continuous strands made from polyester fibers. | Dress fabrics, sportswear, and home furnishings. |
| Polyester Staple Yarn | Short lengths of polyester fiber twisted together. | Knitted and woven fabrics, linings, and stuffing. |
| Recycled Polyester Yarn | Yarn made from recycled PET bottles and textile waste. | Sustainable fashion, outdoor wear, and eco-friendly products. |
| Polyester Microfiber Yarn | Ultra-fine strands that offer a soft touch and high absorbency. | Activewear, intimate apparel, and cleaning products. |
| Textured Polyester Yarn | Yarns with a crimped or twisted structure for added texture. | Apparel, curtains, and upholstery. |
Advantages of Polyester Yarn Over Other Fiber Types
Polyester yarn is gaining popularity in the textile industry. It offers several advantages over other fiber types. First, its durability stands out. Polyester is resistant to stretching and shrinking. This means clothing retains its shape longer. Reports indicate that polyester fabrics have a lifespan 30% longer than cotton.
Another significant advantage is polyester's moisture-wicking ability. It transports moisture away from the body. This feature is crucial for sportswear. Athletes prefer polyester for comfort during workouts. Additionally, polyester resists stains better than natural fibers. This quality reduces the need for frequent washing and helps maintain garment appearance.
Tips: When choosing polyester blends, consider the desired texture. Blends can enhance softness while maintaining durability. Be mindful of the potential for static cling in dry conditions. Adjust fabric finishes to counter this issue. While polyester is advantageous, consider incorporating different fibers for breathability and comfort.
Professional studies reveal that the global polyester market is expected to grow by 4.5% annually. This indicates a strong trend toward synthetic materials in fashion. However, there are environmental concerns linked to polyester production. Sustainable practices are essential to minimize ecological impact.
Future Trends in Polyester Yarn Development and Applications
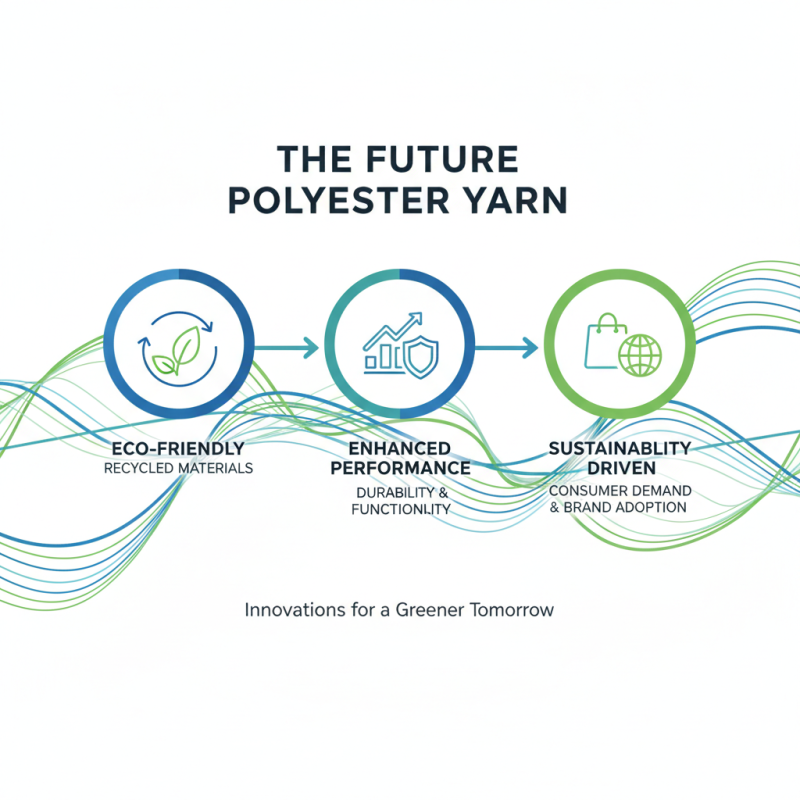
The future of polyester yarn development looks promising. Innovations focus on enhancing performance and sustainability. Next-generation polyester yarns are increasingly eco-friendly. These yarns often use recycled materials, reducing waste. This shift aligns with consumer demand for greener products. Brands adopt practices that minimize environmental impact.
Tips: Consider using recycled polyester in your own projects. It's available in various colors and textures.
Smart textiles are also on the rise. Polyester yarns are engineered to add functionalities. For example, moisture-wicking properties enhance athletic wear. These yarns can also offer UV protection and antimicrobial features. However, this technology is still evolving. Some options may not perform as expected.
Tips: Test yarn samples before large-scale production. This ensures quality and functionality meet your needs.
The integration of digital technologies further drives development. 3D knitting and weaving techniques create unique fabric designs. Manufacturers can respond swiftly to trends. Still, adapting to this fast pace can be challenging. Not all companies can keep up, leading to inconsistent quality.
Related Posts
-
Top Benefits of Using a Cone Winding Machine for Efficient Yarn Production
-
How to Choose the Best Yarn Bobbin Winder for Your Knitting Projects
-
How to Choose the Best Weaving Machine for Your Textile Business in 2025
-

Unlocking Efficiency and Precision with the Advanced Bobbin Winder Sewing Machine for Seamless Projects
-

How to Choose the Best Bobbin Winder Machine for Your Sewing Needs
-

10 Best Yarn Types for Weaving Looms in 2023: A Comprehensive Guide
